-
Products
-
- Featured Products
- Supraflex Cruz
-
- Professionals
- Patients & Caregivers
- Investors
- About SMT
Main navigation
What are the symptoms?
Coronary artery disease progresses over the years. Therefore, symptoms appear gradually as the plaque builds up. These symptoms may be experienced under stress, during physical activity or even at rest. Symptoms are not common for all and may be different for men and women. Symptoms included are:
- pain in the upper body
- shortness of breath
- fatigue
- irregular heartbeat
- sweating
- nausea
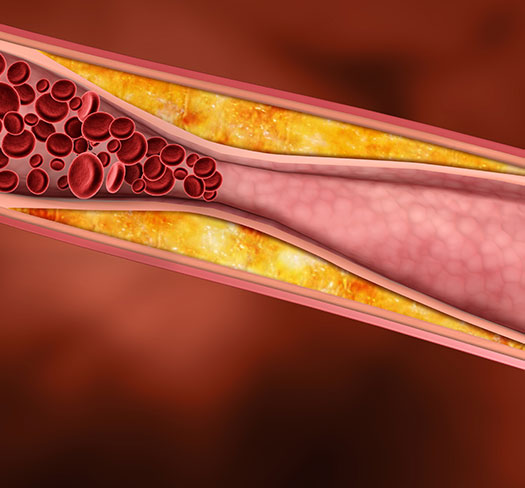
Risk factors may be divided into two categories: modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors.
1. Non-modifiable risk factors are those factors which cannot be changed. These include:
![]() age above 45 years for men and 55 years for women
age above 45 years for men and 55 years for women
![]() male gender
male gender
![]() race
race
![]() family history of heart disease
family history of heart disease
2. Modifiable risk factors are those factors which may be changed through lifestyle changes. These include:
![]() smoking
smoking
![]() high blood pressure
high blood pressure
![]() high cholesterol levels
high cholesterol levels
![]() high alcohol intake
high alcohol intake
![]() diabetes
diabetes
![]() overweight/obesity
overweight/obesity
![]() lack of physical activity
lack of physical activity
![]() high stress levels
high stress levels
![]() unhealthy diet
unhealthy diet
Risk factors occurring together increase the risk for coronary artery disease.
Coronary artery disease may be diagnosed through:
- Blood tests
- Electrocardiogram
- Echocardiogram
- Stress Test
- Heart CT scan
- Cardiac Catheterization
- Angiogram

Treatment of coronary artery disease may be done through:
- Lifestyle changes:
- Quitting smoking
- Controlling conditions of high blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Weight loss
- Managing stress levels.
- Medication:
- Cholesterol-modifying medications
- Aspirin
- Beta blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Nitroglycerin
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
- Surgical procedures:
- Coronary artery bypass graft
- Balloon angioplasty
- Stent placement

If you experience the symptoms of coronary artery disease, it may be time to see a doctor. The doctor will ask you to describe your symptoms, the duration and what physical activity was being carried out when it occurred. Diagnostic tests will then be performed to confirm a diagnosis. If the symptoms are ignored, the disease may progress fast and result in a heart attack and cause permanent damage.


